Feb 19
2025
Support for S-102 Edition 3.0.0
As one of the first in the market, CARIS BASE Editor 6.1.20 now supports the initial operational edition (3.0.0) of the IHO S-102 product specification. With the newly added process, users can export gridded data into an S-102 Exchange Set with true S-100 compliant folder structure, dataset file naming, and exchange metadata.
During export, a CATALOG.XML file will be created to record S100_ExchangeCatalogue metadata. These metadata entries will be automatically populated from a default template (an example is provided in the installation folder) as well as some user options. Efforts have been made to require only dataset-specific metadata to be specified through user options, minimizing manual work.
An additional S-100 license is required to use this new function. CARIS Easy View 6.1.20 was released to support the display of the new S-102 Edition 3 dataset.
Sep 25
2023
Automation
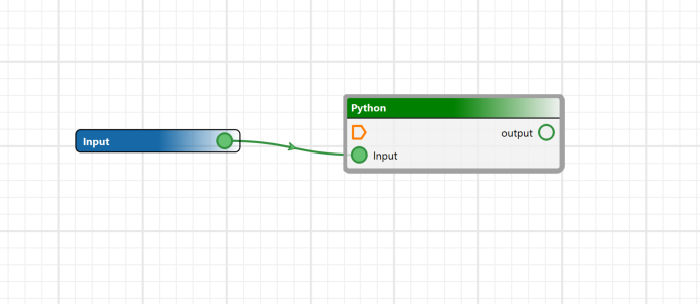
To integrate with third-party solutions or to include with individual business logic, BASE Editor can now use custom processes written in python scripts and use CARIS Process Designer to add them inside a process model. Additionally, CARIS Batch can now be used to launch process models. The combination of these functionalities enhance CARIS automation tools making it possible to execute automated workflow across CARIS applications.
These different tools provide the ability to use a single application as a hub to launch automated workflows.
Python Support
Python scripting is the most flexible way to use CARIS Bathy DataBASE for automating workflows and support is now available for version 3.9, 3.10 and 3.11. Updating to new versions of Python helps safeguard IT infrastructure so join CARIS in upgrading today. Based on in-house testing, upgrading from Python 3.5 or 3.7 to 3.9, 3.10 or 3.11 should have minimal impact on user scripts.
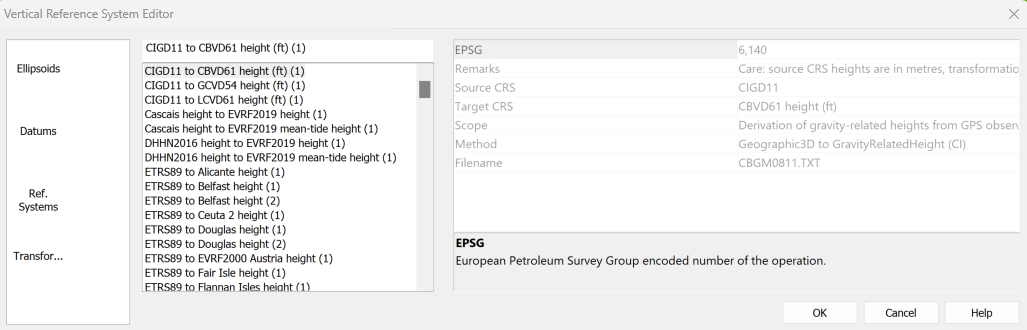
On-the fly transformation
With the release of CARIS BASE Editor 6.1, new tools are available to apply vertical transformations using EPSG registered vertical datums. To provide more flexibility for customers, BASE Editor 6.1 provides the ability to create your own vertical datum using customers' own transformation models.
In addition, a new "on-the-fly" feature delivers vertical transformation to visualize data using a 3D coordinate reference system.
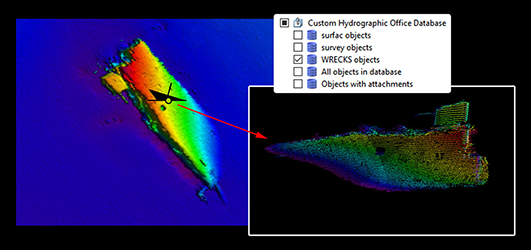
Connect to CARIS Cloud
CARIS BASE Editor now provides the ability to configure a connection to a CARIS cloud tenant. CARIS BASE Editor users can visualize the portfolio of data and products distributed through CARIS Cloud tenants.
Sep 12
2023
Publication to CARIS Cloud via Bathy Data Service
Dec 01
2020
Direct LAS Support
Lidar surveys are the most efficient way to map difficult or dangerous nearshore areas and are one of the fastest growing mapping technologies. Whether mapping from plane, drone or by ship, the use of lidar systems allow for surveys to be conducted safely from a distance. Bathy DataBASE (BDB) fits smoothly into lidar processing pipelines as it's the perfect toolkit to bring together nearshore lidar with offshore multibeam data during the compilation stage of a Ping-to-Chart workflow. The natural next step in expanding lidar capabilities in BDB for our users was through the addition of direct open and edit support for the most popular lidar interchange format. Working with lidar data in LAS 1.4 format is now a seamless experience without the need to import to CSAR while editing. Here are some things BDB can help you get started with lidar data:
- Cleaning and classifying lidar points in Subset Editor
- Creating vector S-57 objects directly from the point cloud in Subset Editor or the 3D Viewer
- Recording video fly-throughs bringing together imagery and chart information with your cleaned lidar point cloud data
New Python Support
Python scripting is the most flexible way to put Bathy DataBASE to work automating workflows, and now, users can enjoy support for version 3.7. Updating to new versions of Python help safeguard IT infrastructure so join CARIS in upgrading today. Support will continue for Python version 3.5 in Bathy DataBASE to allow smooth transitioning for clients with custom scripts, however, Python 3.4 support has been retired. Based on in house testing, upgrading from Python 3.5 to 3.7 should have minimal impact on user scripts.
New Tools and UX Enhancements in Process Designer
Continuing to build on BDB's industry leading bathymetry compilation toolkit, a host of new tools are available as CARIS Batch Processes to achieve full automation of contour creation for Cartography. These new tools are designed to further reduce the need for manual intervention of Cartographers in the product compilation pipeline.
Check out some of the new Cartographic tools to help you automate your workflows:
- Easily generate LNDARE objects within shore lines
- Find and expand isolated shoals to be suitable size for required chart scale
- Find and remove tiny deep contours
- Allow bridging between contours of the same depth level within an allowable distance
- Create depth areas from smoothed and edited contours
- Users can densify line and boundary objects
- Repair Undershoots and Overshoots by aligning contours nearby features and removing duplicate edges with precise snapping
- Convert input features to a new feature type
Other user enhancements to Process Designer Include:
- Adding comments and organizational boxes to help annotate process models
- View and insert user generated Process Models from the Tools list
- Provide default values to Process Models
Apr 28
2020
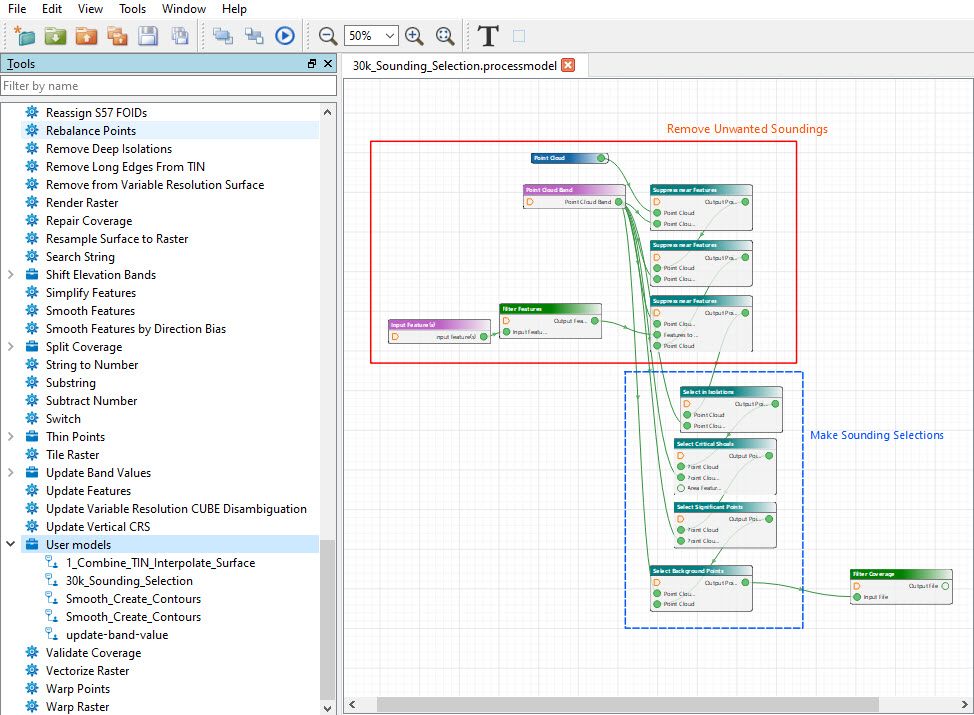
Smart Sounding Selection for Cartography
Bringing automation into chart production required a smart sounding selection process to mimic the selection process of a trained cartographer. To reduce turnaround time and human effort, a new toolkit called Classify Points for Cartography was created to provide that cartographic sounding selection. Users transition from raster surfaces and thinned point clouds, to suppressing undesirable points near other charted objects and selecting points in contour isolations and critical shoals. These complex logic processes are essential to a smart sounding selection before background soundings can be selected to fill the remainder of the product.
The new Classify Point tools are customizable for any chart scale and fit seamlessly into a process design or CARIS Batch process. This offering completes workflow automation with existing surface smoothing and contouring functionality to meet all modern charting needs.
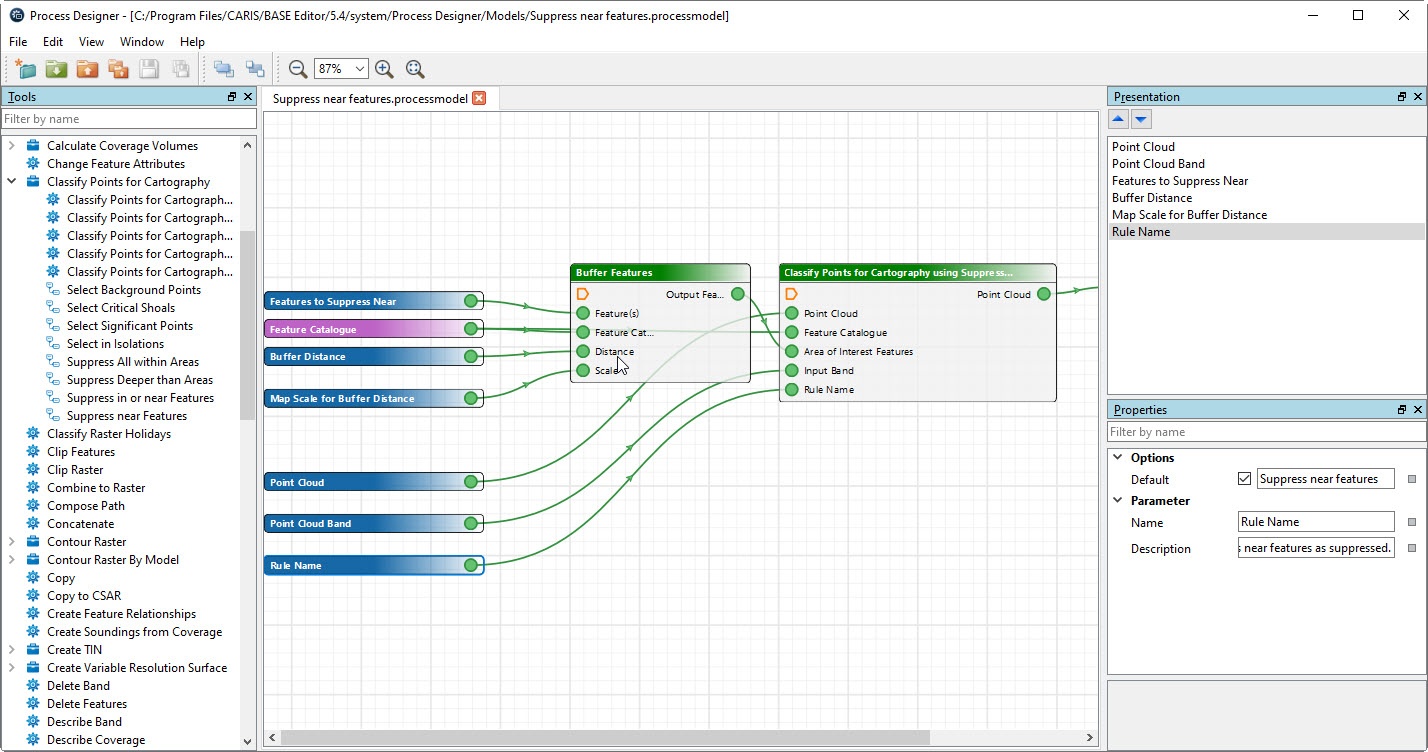
User Experience Enhancements and New Tools in Process Designer
A variety of new functionality is available to enhance the user experience in Process Designer. Delivering automated workflows is the priority for many hydrographic organizations and Teledyne CARIS is meeting that need by expanding the way users can develop intuitive process models.
- When running a process model in the application, a new checkbox is available to log process information to the Logs folder of the application when the process completes. This stores additional information, such as the parameters specified for the process, the inputs, and when the process was run.
- A Presentation window is now available to arrange the order parameters are shown to the user when running a process model.
- Parameters can now be configured with default values which can be adjusted when a user runs a process model in the main application.
- A switch process was added to allow forked processing paths.
- TIN processes have been added to Process Designer. Users can now Create TINs from Coverage or HOB, Remove Long Edges, Add to TIN (for points and breaklines), Extract TIN, and interpolate a raster surface from the TIN. These tools are particularly helpful when integrating data from historical and outside agencies into the main chart production pipeline.
S-100 and S-101 ENC Support
An S-100 module is now available in BASE Editor with S-57 Composer to allow creating and modifying files based on S-100 standards. Even without the module, users can open S-101 ENC files for use as background data in BASE Editor. When opening the S-100 files, updates in the same directory as the main file are now also loaded and applied. Teledyne CARIS is proud to be leading the industry with our S-100 support in our full production suite.
Mar 18
2019
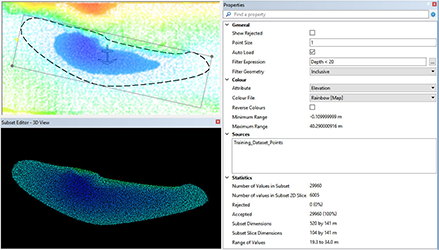
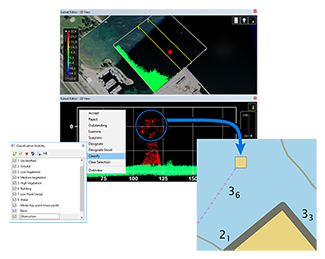
Usability enhancements for point editing
Increasingly, Subset Editor is used not just to validate but to clean, classify and identify features in georeferenced data points from both sonar and lidar surveys. New options are provided to bring efficiencies to this workflow including:
- Colouring based on the data range of the current subset, or the full data range of the sources,
- Colour maps automatically adjusting as data points are flagged, and
- Drawing flagged points, such as Designated, Outstanding, and Examined points, as larger spheres to improve the visual cues for decision-making.
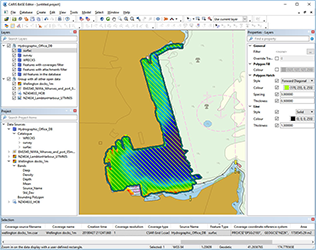
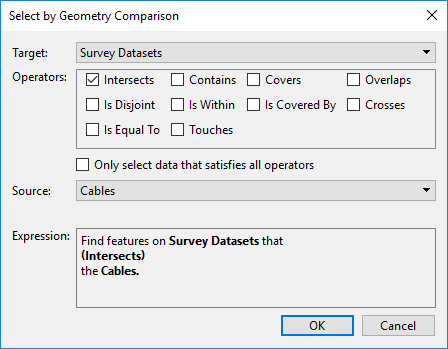
New spatial query
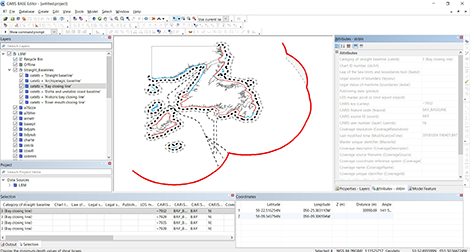
As more datasets are managed in BDB databases, it is critical to quickly locate the data you need for the task at hand. To this end, a new spatial analysis tool is introduced that provides the ability to select features using existing geometry from any vector source. This can be used, for example, to find all the features within an administrative area, to find all charted features that fall within a survey, or (as shown in the image) to find all survey datasets that intersect with an undersea cable.
This spatial query capability is not limited to BDB databases; it can be used when working with any supported sources such as shapefiles, GeoPackages and Web Feature Services.
Time-dependent transformation
BASE Editor is the first CARIS software solution to support time-dependent transformations. These coordinate reference system (CRS) transformations have an epoch component that allows for more precise positioning of data.
Commute a license for travel
The License Manager can now be used to check out licenses from a network license server for a defined period of time. These commuted licenses are temporary local licenses that can be used during surveying when the network license server cannot be accessed.
Oct 30
2018
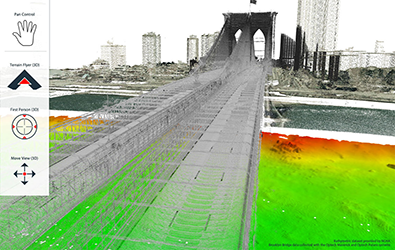
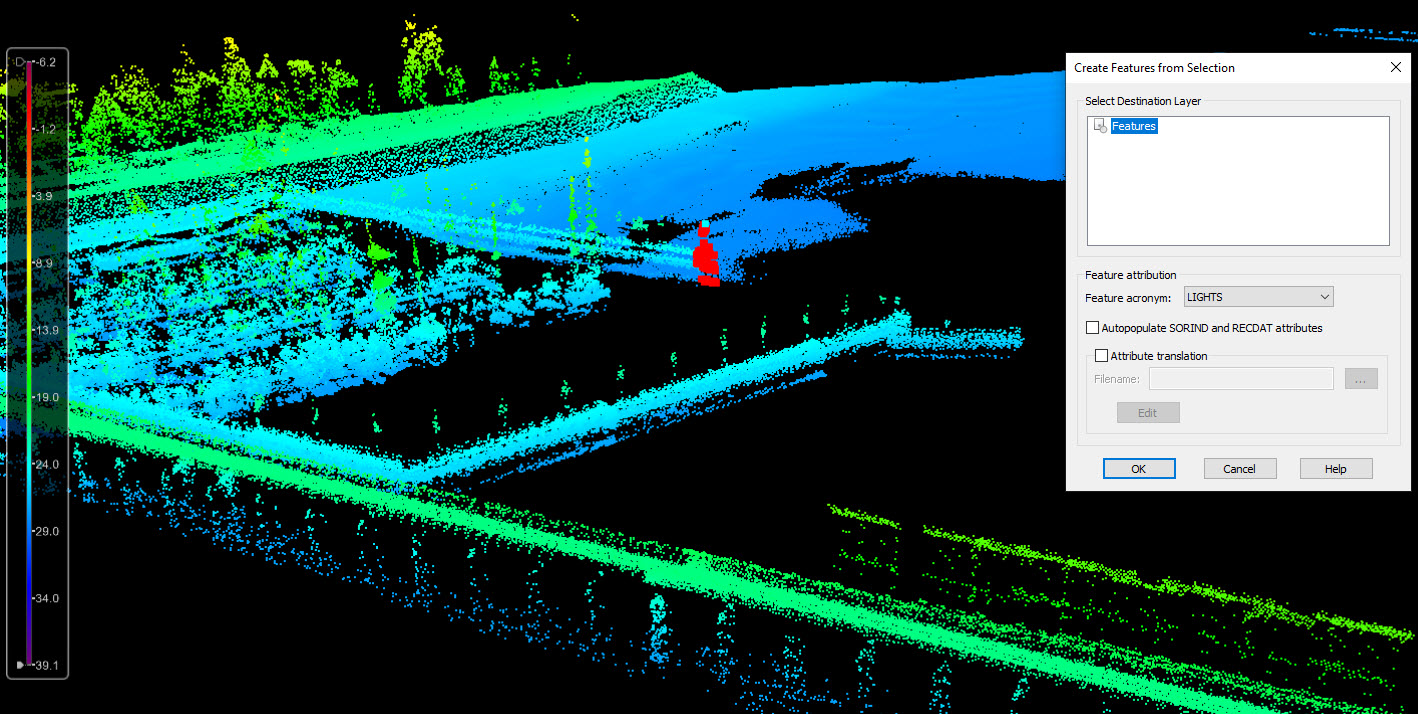
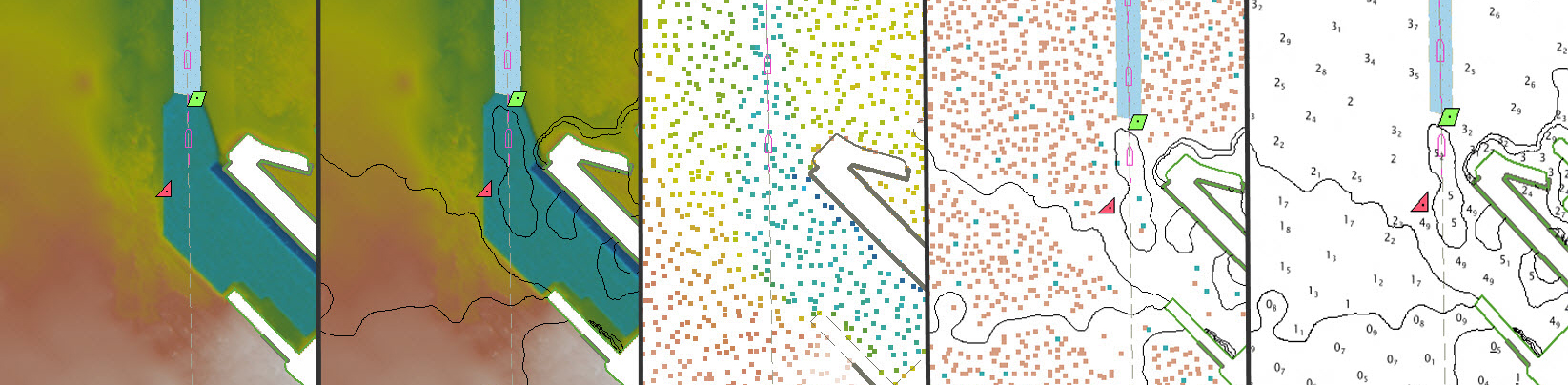
Update chart features with bathymetric lidar
A new workflow well-suited to performing quality control and building a feature set for hydrographic charting from lidar data is available in CARIS BASE Editor. Bring LAS/LAZ data into the BASE Editor environment to assess quality, adjust classification and compare against other data sources. Identify relevant features from point data and imagery and easily model as S-57 features directly in the area-based cleaning tool. Model as a DEM using CUBE or other gridding methods and combine with data from other sensors to generate a full picture of the seabed and shoreline.
Some of the new capabilities to explore:
- Creating cartographic features like rocks and obstructions directly in the Subset Editor while cleaning or QC-ing the data
- Using the flexible expression and geometry filters to isolate data points
- Bringing in reference data (DEMs, imagery, scanner data, etc) to help provide context and adjust flags or classifications with a single click
- Exploring the new Subset Editor controls including new context menu options, short-cut keys and rotation controls
- Adding uncertainty estimates to data points using the Add Computed Band process
New automated techniques for generalizing bathymetry
Building on BASE Editor's industry leading bathymetry compilation toolkit, two new surface preparation techniques have been added along with several workflow improvements.
A new surface smoothing method called Restrained Laplacian was added that is generally less aggressive and results in less smoothing in X,Y and Z planes than our original (Cumulative) Laplacian smoothing. The effect is that the shape of sloped areas such as along a dredged channel remain largely in place with minimal narrowing of the channel.
The surface smoothing processes can now be run on elevation data that has been simplified in advance using a new Rolling Coin technique. This technique was developed by the Finnish Transport Agency as way of achieving an unambiguously safe for navigation contour set by imposing a pixel-based mask that pushes elevations into the shoaler depth ranges. The effect of the Rolling Coin is a double-buffered surface that produces contours that are greatly reduced in number and complexity than from the original dataset.
The Rolling Coin technique produces the best results when used in conjunction with Laplacian Smoothing and/or vector Contour Smoothing processes. These processes work together in a manual or fully-automated workflow to produce topologically sound, ‘chart ready’ and safe for navigation contours. These results hold even for high resolution contours such as on bathymetric ENC (bENC) overlays where there is little tolerance for topology issues or cartographic manipulations requiring manual adjustments.
Further enhancing the bathymetry compilation workflow are the additions of a new option to directly model shoal-biased thinned points as Sounding features in automated workflows, new safe-guards against producing crossing contours with vector Contour Smoothing and enhanced error reporting.
New Licensing Technology
Bathy DataBASE is the first CARIS release to incorporate our new licensing technology. This upgraded licensing is softkey based, so no physical dongles are required; a license Entitlement will be created for software activation.
Key benefits of this new technology include:
- Convenient and easy softkey activation
- The elimination of physical hardware removes the possibility of damage or loss
- No more need of a separate licensing tool
- Faster software purchase and setup
- Improved license usage transparency for network license users
For more information about the new licensing technology and how it will affect your organization contact Customer Services, or visit License FAQ.
Manage LOTS Limits and Boundaries in Bathy DataBASE Server
Maritime limits and boundaries generated with CARIS LOTS can now be managed in Bathy DataBASE Server. New LOTS catalogue and portrayal files are available to use to set up a database, and then data can be imported, moving your data management into a relational database environment.
May 03
2018
New scope for BDB Server
As part of expanding the scope of activities that can be supported in BDB Server, databases now supports both feature and coverage data management. The object and attribute model is now fully exposed to the user and can be customized to include any point, line or polygon feature types as required by the customer. This allows the role of BDB Server within an organization to expand beyond the management of bathymetric DEMs and into new areas of data management for features (such as for wrecks or administrative boundaries) and coverages (such as backscatter mosaics or Lidar point clouds). New feature portrayal options allow for styling that can be tailored for use of the system in different domains such as charting, oil and gas exploration and port and waterway management.
Subset Editor data filtering
Interacting with the data that you want to in Subset Editor has never been easier. There are new geometry and attribute-based filters available that limit the data loaded into Subset Editor, allowing very quick isolation of points of interest in a specific area. The filters can be toggled independently, allowing quick access to points for cleaning or classification.
Flexible interface for organizing and interacting with data
To support the changing needs of the modern hydrographic office, CARIS is pleased to provide a redesigned application interface that gives users new tools for managing and deriving information and products from diverse sources of data. With expanded access to GIS formats such as GeoPackage, services such as Web Feature Services, and direct connections to databases such as PostgreSQL, new possibilities emerge for integrating and expanding the use of CARIS applications within an organization.
The new application interface provides a consistent user experience when connecting to different data sources, filtering, grouping, setting up display properties and portrayal instructions.
Navigation controls
BDB is an effective platform for exploring geospatial data. New navigation options have been added to make interacting with data easier and more intuitive including a new Pan navigation mode and the addition of the 3D View Controls Types in the toolbar. The user can set the preferred navigation modes and transition seamlessly between the 2D and 3D Views.
Expanded Python API
A new Python API module has been added to support interacting with vector data in a wide variety of formats New capability has also been added to the coverage and BDB Server modules, to allow scripting a wider variety of workflows, with goals of simplicity, usability, and versatility.
For example, a Python scripts can now be used to automatically populate vector feature attributes whenever a feature is created, or when a feature is edited, or when an associated coverage is uploaded to the database. A very simple example is to automatically populate the Recording date attribute when a feature is created, which can be accomplished with just a few lines of code
import datetime
def feature_created(newFeature):
newFeature.attributes['RECDAT'] = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d")
Process Designer
Process Designer has several usability updates to make it easier to design and validate a processing workflow. These updates include applying a modern design which makes it easier and more intuitive to interact with the application and design a Process Model
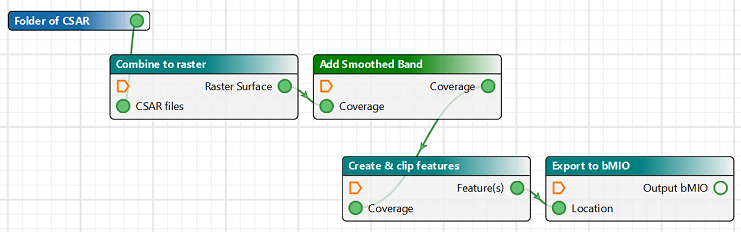
It is now possible to include a Process Model inside another Process Model using File > Insert Model. This makes it easier to manage complex Process Designer models by defining common capability once and re-using it multiple times. In the example below, a Process Model for creating a bMIO has been created from the Add Smoothed Band process and three existing models, which are clearly identified by their teal colour.
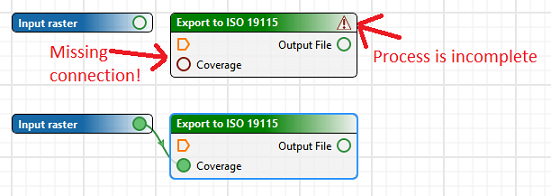
Validation has been built into the Process Designer, making it clear to a user if they have not defined a required parameter or connection. In the example below, the process is showing that it requires a connection for the "Coverage" input.



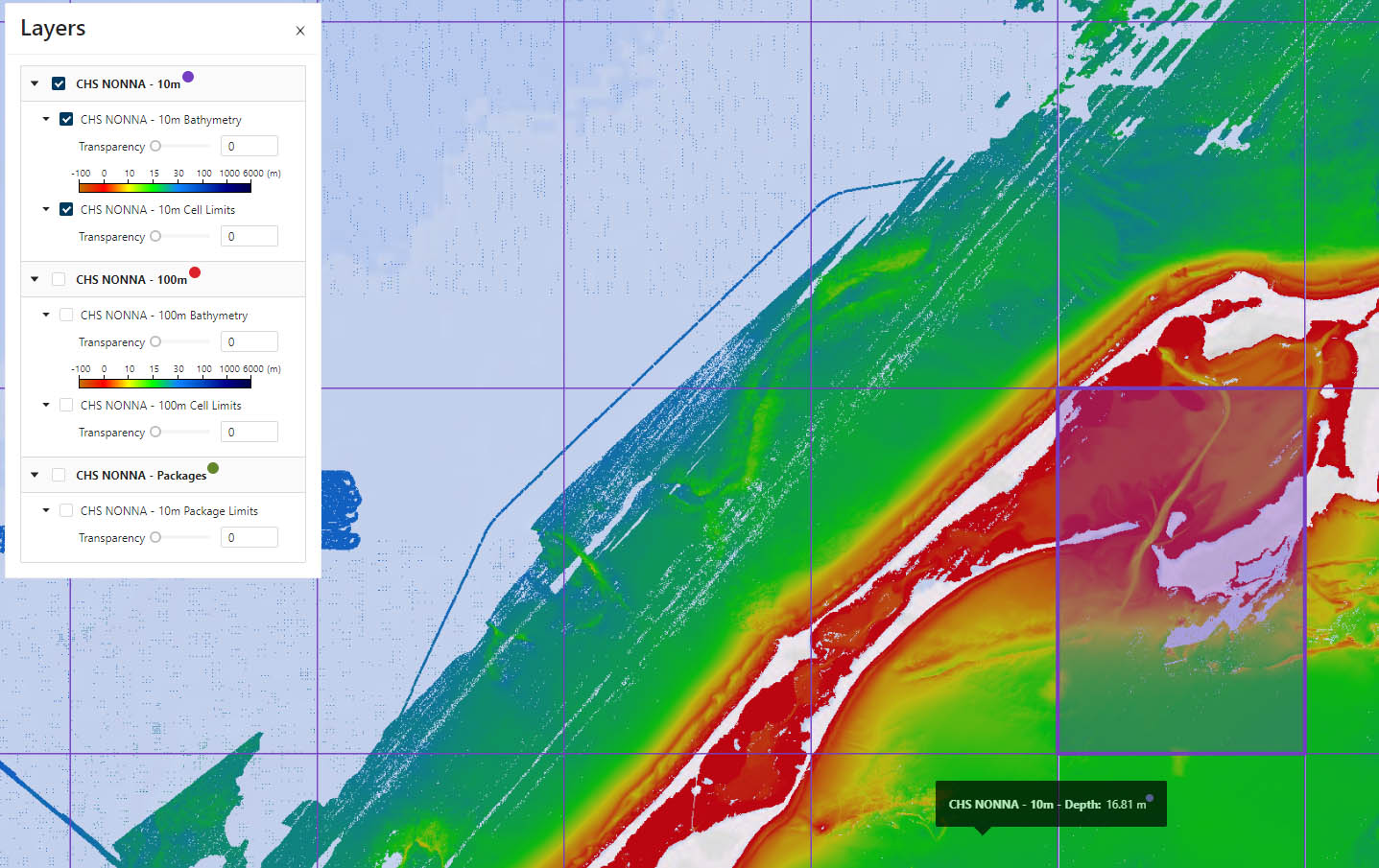 CHS NONNA 10m resolution cells selected in CARIS Cloud's catalogue of products. Data courtesy of the Canadian Hydrographic Service
CHS NONNA 10m resolution cells selected in CARIS Cloud's catalogue of products. Data courtesy of the Canadian Hydrographic Service
 With the participation of the Canadian Hydrographic Service.
With the participation of the Canadian Hydrographic Service.
 Lidar to chart in BASE Editor
Lidar to chart in BASE Editor
 Limits and Boundaries in Bathy DataBASE Server
Limits and Boundaries in Bathy DataBASE Server